As shown in the figure, use a laser with a continuous power of 0.25-16kw or a pulse laser with a frequency of more than 100Hz to gather the beam into a light spot with a diameter of 0.01mm or less through the optical system, so as to obtain an energy density of the 8th power of 10 to the 10th power of 10 w/ cm2 and a high temperature of 10000 ℃.
Then, no matter whether the focus is on the workpiece surface of any hard material, once the workpiece surface absorbs energy, it will instantly melt or vaporize the material locally. After melting, the liquid metal or non-metal that has not vaporized will be heated and cleaned by blowing oxygen beam.
Depending on the nature of the workpiece material, auxiliary airflow such as nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, argon or compressed air can also be used to remove the liquid metal from the cut and protect the cutting surface. At the same time, by accurately controlling the spot size and the distance from the focus to the cutting surface, a smooth cutting section can be obtained.
Laser cutting is a cutting method often used in the production of stainless steel cabinets. Manufacturers of stainless steel cabinets should master this technology.
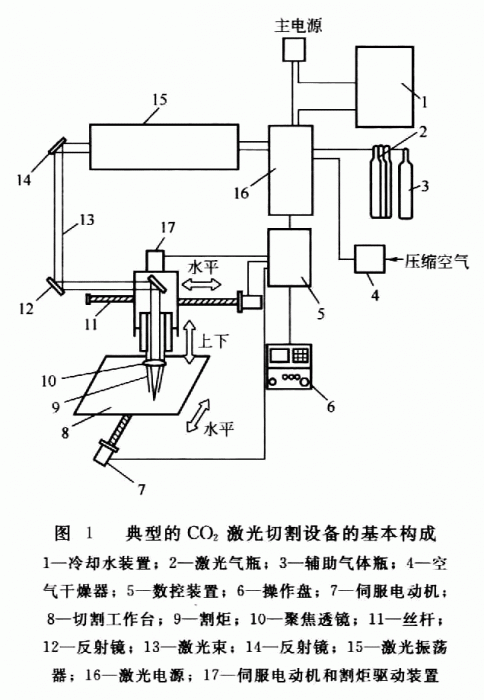
Basic principle diagram of laser cutting